Nigerian Hacking Group Targets Shipping Firms
Network security firm Secureworks has identified a Nigerian threat group that appears to be focused solely on the marime industry. The group, dubbed "Gold Galleon," uses basic email scams and publicly available hacking software to try to steal hundreds of thousands of dollars from unsuspecting ship managers and service providers.
According to Secureworks, Gold Galleon is a group of about 20 individuals who work together to hack maritime firms all over the world using basic techniques. They rent hacking tools for just a few dollars per month; they communicate via Skype; and they identify targets using online company directories and commercially-available contact lists.
While the criminal gang uses an online proxy service to disguise its location, several cues indicate that it is of Nigerian origin, Secureworks said. The group communicates in Nigerian Pidgin, an English creole language, and it uses phrases assocated with a Nigerian social organization called the "Buccaneeers Confraternity" for usernames and passwords.
Simple methods, big rewards
Once the group has identified a new target, it sends a spearphishing email carefully tailored to the recipient. The email has an attachment containing malware, which deploys on the unsuspecting victim's computer and logs his or her keystrokes, recording the username and password for the victim's business email account. Once the account is compromised, the group uses a software tool to collect all the email addresses with which that user has had an interaction, and it sets itself up to intercept business transactions between the user and his or her clients.
Many maritime firms use email to handle invoicing and payment details. When the Gold Galleon group sees payment details relayed on an invoice in a compromised email account, it intercepts the invoice, alters the account numbers to direct the money to its own "mule" bank account instead, and uses a similarly-worded email address to send the altered request on its way to the intended recipient. Often, the buyer will not detect the change to the sender's email address and the bank details, and will simply pay the fraudulent invoice.
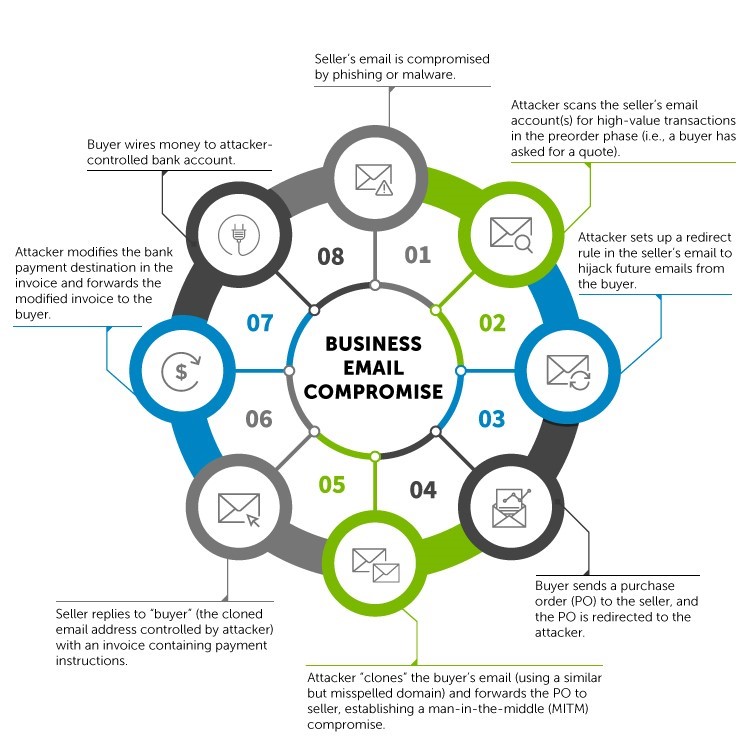
Graphic courtesy Secureworks

that matters most
Get the latest maritime news delivered to your inbox daily.
In one case study, the group was able to steal email usernames and passwords for eight employees at a South Korean shipping firm, including the accountant's account. Gold Galleon members monitored the company's financial transactions to gain familiarity with its billing cycles and clients. Then, when the South Korean firm initiated a $50,000 "cash to master" transaction to deliver money to one of its vessels, a Gold Galleon hacker impersonated the recipient and asked for payment to be sent to a "subsidiary account for now" because of unspecified bank issues. Secureworks was monitoring the exchange and notified the parties involved that they were being hacked, and it thwarted two subsequent attempts on the same firm - one for $234,000 and another for $325,000.
Secureworks warned that smaller shipping firms may be exposed to heightened risk as threats like Gold Galleon focus on targets that are susceptible to simple hacking - in this case, a basic "business email compromise" (BEC) scam. The firm advised that two-factor authentication for business and personal email is a key step, since most BEC threat groups use a webmail portal to break in. Two-factor authentication is a familiar verification tool that relies on the legitimate user having an object (like a smartphone or a magnetic keycard) on his or her person, in addition to the account password. It is difficult for low-end hackers to defeat, but it is not often used by small and medium businesses.
