Atlantic Hurricane Season Comes to an End
The 2019 Atlantic hurricane season, which ends on November 30, was marked by tropical activity that churned busily from mid-August through October.
The season produced 18 named storms, including six hurricanes of which three were “major” (Category 3, 4 or 5). NOAA’s outlook called for 10-17 named storms, 5-9 hurricanes and 2-4 major hurricanes, and accurately predicted the overall activity of the season.
This year marks the fourth consecutive above-normal Atlantic hurricane season. The only other period on record that produced four consecutive above-normal seasons was 1998-2001. Also this year, five tropical cyclones formed in the Gulf of Mexico, which ties a record with 2003 and 1957 for the most storms to form in that region. Of those, three — Barry, Imelda and Nestor — made landfall in the U.S.
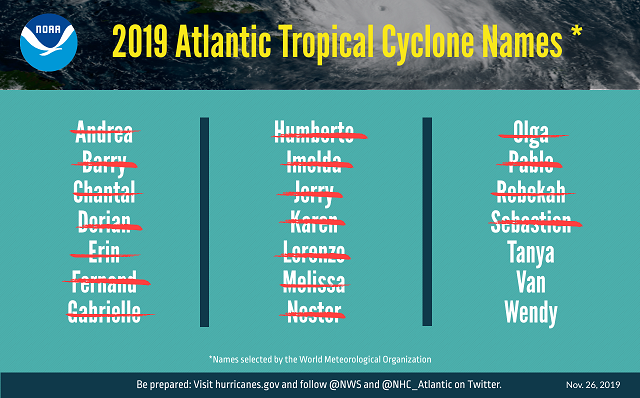
A graphic listing 2019 Atlantic tropical cyclone names selected by the World Meteorological Organization. The 18 named storms that formed are designated with a red slash through their name. They are listed in alphabetical order: Andrea, Barry, Chantal, Dorian, Erin, Fernand, Gabrielle, Humberto, Imelda, Jerry, Karen, Lorenzo, Melissa, Nestor, Olga, Pablo, Rebekah and Sebastien.
The three major hurricanes this season were Dorian, Humberto and Lorenzo. Hurricane Dorian is tied with three other hurricanes — the 1935 Labor Day Hurricane, 1988’s Hurricane Gilbert and 2005’s Hurricane Wilma — as the second strongest hurricane on record in the Atlantic basin in terms of wind (185 mph). In all, four storms made landfall in the U.S. during the 2019 season: Barry, Dorian, Imelda and Nestor.
“This season’s activity ramped up in mid-August during the normal peak of the season, as we predicted,” said Gerry Bell, Ph.D., lead seasonal hurricane forecaster at NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center. “The above-normal activity is consistent with the ongoing high-activity era, driven largely by the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation, which entered a warm phase in 1995. Conditions that favored more, stronger, and longer-lasting storms this year included a stronger West African monsoon, warmer Atlantic waters, and weak vertical wind shear across the western Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico.”
An average season has 12 named storms, six hurricanes, and three major hurricanes.
During the 2019 season, NOAA’s hurricane hunter aircraft and crews flew 57 missions over 430 hours, which along with the 53rd Weather Reconnaissance Squadron of the Air Force Reserve, provided critical data that aided in storm forecasting and research.
In addition, NOAA’s King Air crew collected more than 26,939 aerial images covering more than 4,300 square miles of areas affected by Hurricane Dorian, including shoreline, ports and impacted inland areas of several Bahamian Islands to aid in emergency response.
NOAA and NOAA-supported researchers from the U.S. and Caribbean deployed 30 autonomous ocean glider missions in the Atlantic this season, which provided more than 75,000 observations of ocean temperature and salinity to operational hurricane forecast models. Ocean temperature and salinity data provide important clues about hurricane intensification.

that matters most
Get the latest maritime news delivered to your inbox daily.
The 2020 hurricane season will officially begin on June 1 and NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center will provide its initial seasonal outlook in May.
Source: NOAA
