Furukawa Battery Meets the Challenges of the Energy Transition

As the global economy adapts to the transition away from carbon-based sources of energy there is an increased focus on the use of renewable energy to provide a zero-emission source of electrical power. An integral part of the solutions that provide these sources of power are batteries and energy storage systems with The Furukawa Battery Company of Japan (Furukawa Battery) being one of the leading companies in this field.
Furukawa Battery is a Japanese company that traces its origins back to 1914 when Furukawa Electric established its battery factory in Amagasaki City, Hyogo Prefecture, and started production of lead-acid batteries. In 1950 Furukawa Electric spun-off its battery business and Furukawa Battery as a separate company was formed. Since then, the company has continued to evolve & expand and now employs over 2,400 people. In 1992 it also expanded overseas and established Siam Furukawa Battery Co., Ltd. in Thailand and in 2013 established Furukawa Indomobil Battery Manufacturing (FIBM) in Indonesia.
In addition to being a manufacturer of high-quality batteries and power supply devices the company is also a leading innovator and has engineering research and development divisions located at several locations, with the Innovation Laboratory in the Iwaki Plant being one of its key development sites. This focus on research has led to the development of a number of market leading battery technologies including in 2003 the world's first lithium-ion battery for space application. This innovative battery technology was installed in the "Hayabusa" asteroid explorer. The spacecraft “Hayabusa 2” was also equipped with a high reliability, long-life lithium-ion battery supplied by Furukawa Battery.
Another example was the development of the MgBOX – a Magnesium Air Battery that can be used in emergencies and is activated by adding water. This product was launched in Japan in 2014 and was developed based on the experience of the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011. In 2017 as part of its ongoing focus on cutting-edge research, Furukawa Battery also established a next-generation lithium-ion battery development company - ABRI Co., Ltd. (Advanced Battery Research Institute) in conjunction with the Tokyo Metropolitan University.

MgBOX Magnesium Air Battery (Source: Furukawa Battery)
Although there has been much focus on lithium-ion batteries recently, Furukawa Battery has also developed advanced valve regulated lead-acid (VRLA) batteries including the FCR and the UltraBattery® series. FCR batteries are a high quality and long life VRLA battery technology suitable for standby, emergency, cycle and dual use. They are also suitable for applications in which charging and discharging are repeated frequently. These batteries can be used for emergency or back-up power and charged from a range of charging systems including solar power. They can also be used for renewable energy applications. The UltraBattery® is a long-life hybrid battery that incorporates unique ultracapacitor technology. It is suitable for a wide range of applications including land-based and marine renewable energy projects and has been used for a ship-based solar power project.
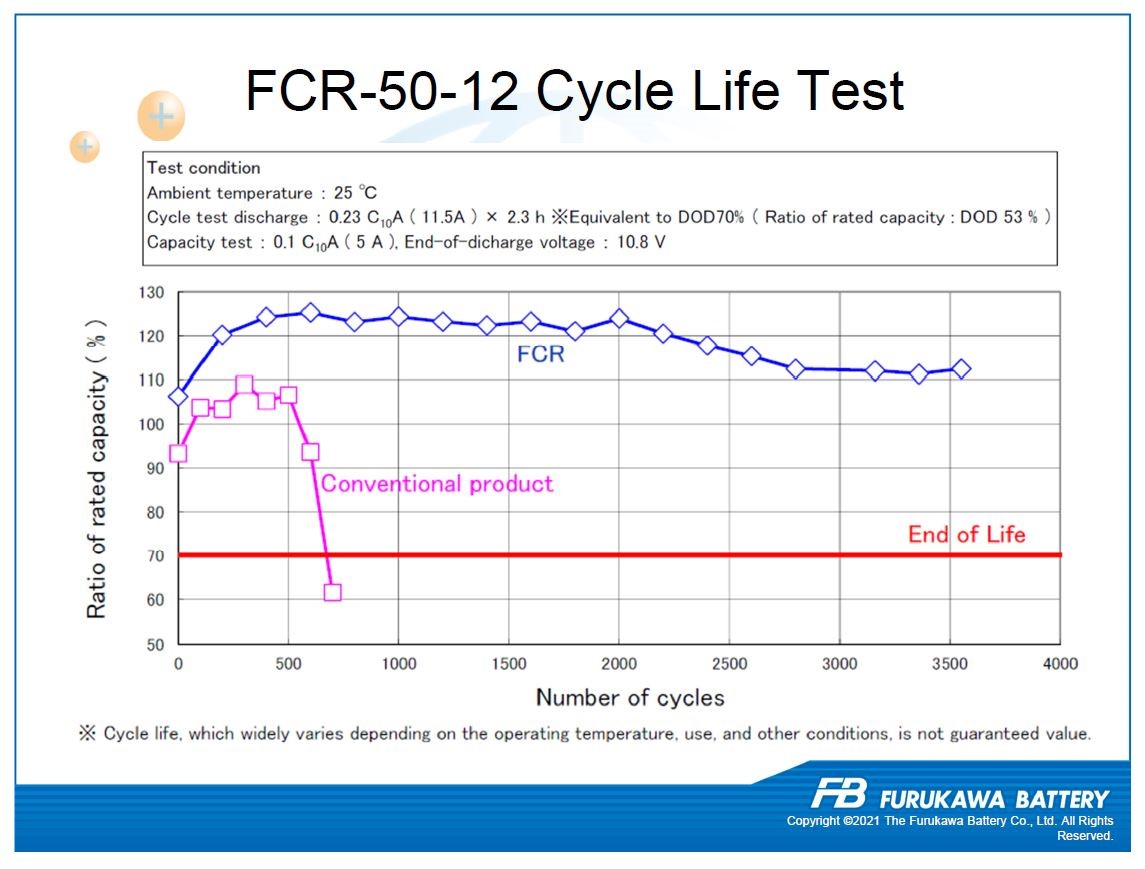
Performance chart for FCR-50-12 battery (Source: Furukawa Battery)
In addition to supplying batteries for a wide range of automotive, transportation & industrial uses, Furukawa Battery has also cooperated with Eco Marine Power since 2014 on promoting the use of batteries on ships including marine solar power systems. Several battery types are also suitable for emergency back-up power on-board ships.
Quality at Furukawa Battery applies not only to the products themselves, but to every stage, every category and every level of corporate activities - from research and development to manufacturing, service and administrative operations. The company continually iterates on a PDCA-based (plan–do–check–act or plan–do–check–adjust) management cycle that maintains and improves the quality of products, services and business operations.
Furukawa Battery also places emphasis on protecting the environment and has an environmental policy that encompasses a commitment to “reducing CO2 emissions and conserving resources throughout the entire life cycle of its business activities including order-taking and agreements, design and development, purchasing, manufacturing and providing service.” The company’s lead-acid batteries are for example over 90% recyclable & solar panels are installed at its production facilities at Iwaki, Fukushima. Another measure taken to protect the environment includes cleaning industrial waste-water to remove pollutants and the company has attained ISO 14001 certification for its environmental management system (EMS). In addition, the Imaichi Plant has received the highest award from the Kanto Branch of the Japan Electric Association for its steady efforts to cut power consumption and the implementation of measures that lead to energy savings.
In 2020 The Furukawa Battery Company of Japan reflected upon the 70 years since it was spun-off from Furukawa Electric and since its formation, it has evolved and expanded, whilst at the same time maintaining its proud heritage and focus on quality. It is now a world leader in the manufacture of batteries and is also at the forefront of developing the new & innovative solutions required for the energy transition.
Greg Atkinson is the Chief Technology Officer (CTO) and founder Eco Marine Power (EMP) in Japan. EMP develops innovative renewable energy systems for shipping including Aquarius Marine Renewable Energy (MRE), the EnergySail and Aquarius Marine Solar Power. His qualifications include a PhD in Maritime Engineering, an MBA, a BSc in Electrical Engineering and an Associate Diploma in Electronic Systems Maintenance. He is also a Fellow of the Royal Institution of Naval Architects (FRINA) and a Fellow of the Institute of Marine Engineering, Science & Technology (FIMarEST).
The products and services herein described in this press release are not endorsed by The Maritime Executive.

