Investors Expect Stronger LNG Demand
Westwood Global Energy expects global LNG capital expenditure to reach $236 billion over the 2018-2022 period, based on its latest analysis of sanctioned and upcoming projects. This represents a 14 percent growth compared to the preceding five-year period.
The LNG shipbuilding business is also expected to recover with over 150 further orders expected to be placed for delivery over the period to 2022.
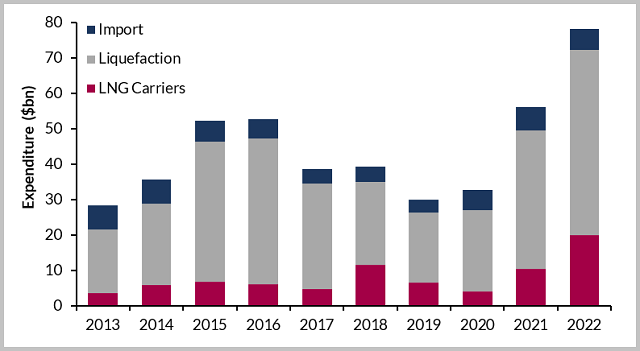
Global LNG Capex by Facility Type 2013-2022
Over the forecast period, the construction of liquefaction terminals will account for 67 percent of the LNG market, with expenditure totaling $157.5 billion. This investment will subsequently lead to an additional 119 mmpta of global export capacity over the 2018-2022 period.
Despite several countries opting for floating regasification units, land-based import terminals remain attractive, with expenditure expected to grow at eight percent over the 2018-2022 period and amount to spending of $25.9 billion.
Over the period, 265 LNG carriers are expected to be delivered, as record numbers of carriers will be required to meet the increased LNG output expected by the end of the forecast period. Of the number of LNG carriers expected to be delivered, 154 are yet to be ordered. Korean shipbuilders will continue to dominate the carrier market, with Daewoo Shipbuilding and Marine Engineering, Samsung Heavy Industries and Hyundai Heavy Industries accounting for 60 percent of the current orderbook.
Air Products’ single mixed refrigerant and ConocoPhillips’ Optimized Cascade process accounted for 54 percent and 46 percent respectively of the liquefaction technology market over the 2013-2017 period. Over the forecast period, Air Products currently has the largest market proportion (74 percent), with ConocoPhilips (20 percent), Shell (four percent) and Linde (two percent) accounting for the remaining proportion of known contracts awarded.
Operators sanctioning new projects are seeing lower supply chain costs and despite current over-supply are expecting a growth in LNG demand that will see supply-demand balance by the mid-2020s.
While long-term contracts are the foundation of the LNG contracting model that underpins returns on investment, changes in the business environment are driving an increase in spot trading and short-term contracts, leading to a rise in the number of spot cargoes.
