AiP Issued for System of Rigid Sails and Solar Power for Eco Ships

In a step towards the realization of a zero-emission power and propulsion for shipping, Japan’s Eco Marine Power received an Approval in Principle (AiP) from ClassNK for its concept for a ship featuring a renewable energy system for ships. Know as Aquarius Marine Renewable Energy (MRE), the system integrates rigid sails, marine-grade solar panels, energy storage modules, a charging system, and computers that enable the ship to tap into renewable energy by harnessing wind and solar power.
Wind power and solar energy are already popular sources of clean renewable energy on land, so Eco Marine Power believes it is possible to develop a system that will allow ships to use these same sources of energy. According to the designers, the Aquarius MRE can be incorporated into existing ship designs or be integrated into newbuilds.
“The certification by ClassNK of Aquarius MRE including our EnergySail, is a major milestone for our project as it covers not only the hardware elements but also the integrated system architecture & computer systems,” said Greg Atkinson, Chief Technology Officer at Eco Marine Power. “We believe our scalable and flexible marine renewable energy system will provide an important source of zero emission power and propulsion for ships and assist the shipping industry meet its decarbonization objectives.”
Included in the scope of the AiP are two main sub-systems that provide the solution. The EnergySail is a rigid sail wind-assisted propulsion system that includes the sail structure, driving system, and automated control system. Aquarius Marine Solar Power is an energy management system to utilize solar power that includes photovoltaic modules, batteries, electrical and control systems. Together these sub-systems are integrated to form Aquarius MRE. Within this system architecture, various other equipment and sensors can also be connected.
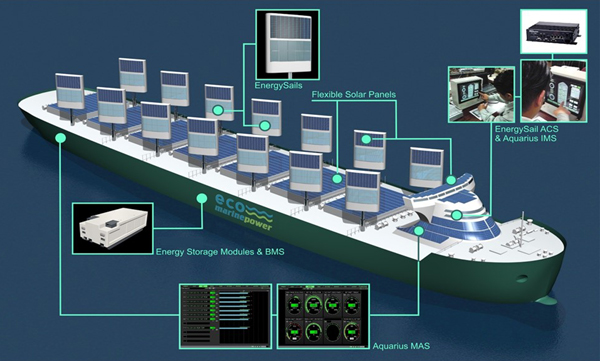
The range of systems integrated into the Aquarius concept (Eco Marine)
The rigid sails are based on EMP's EnergySail technology and can even be used when a ship is at anchor or docked. Each EnergySail can be configured with a mix of sensors, photovoltaic panels, or other power generation devices. The array of rigid sails are automatically positioned by a computer system to best suit the prevailing weather conditions and can be lowered and stored when not in use or during bad weather. When a ship is at anchor or in port, batteries approved for use on marine vessels can provide an alternative source of power.

that matters most
Get the latest maritime news delivered to your inbox daily.
Although the system is being initially designed for large ships, the company says much of the technology will also be suitable for smaller vessels such as coastal freighters, small passenger ferries, tourist boats, and unmanned surface vessels (USV's). Elements of the system are also suitable for offshore marine use and land-based renewable energy projects. A study is also being conducted to determine if it would be feasible to use the system on naval and government vessels, such as patrol ships and marine survey vessels.
The Aquarius MRE development project involves companies working as strategic partners with EMP. This includes KEI System, Teramoto Iron Works & The Furukawa Battery Company. In addition, several shipowners are cooperating with Eco Marine Power planning for sea trials of the system and in studies regarding the use of renewable energy systems onboard ships.
